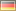
Fadenwürmer (Nematoda)
Nematoden sind kleine, nicht segmentierte, meist farblose Würmer, die besonders arten-und individuenreich in Gewässern und im Boden leben. Daneben gibt es viele an Pflanzen und Tieren parasitierende Arten, z.B. Spulwürmer. Im Boden weisen die Fadenwürmer neben einer hohen Artenvielfalt auch vielfältige Ernährungsweisen auf. Es gibt Bakterien-, Pilz- und Pflanzenfresser sowie Allesfresser und Räuber. Dadurch beeinflussen Nematoden Abbau- und Mineralisierungsprozesse und Nährstoffflüsse im Boden nachhaltig. Sie werden deshalb gerne zur Beurteilung des Zustands eines Standorts (z.B. Agrarflächen) verwendet. Dabei ist die Artbestimmung schwierig und Spezialisten vorbehalten, so dass häufig die Familien- oder trophische Zusammensetzung der Gemeinschaften verwendet wird.
Die Nematodensammlung des SMNK besteht aus 216 Individuen auf 97 Dauerpräparaten von 37 Arten. Darunter sind 125 Typen (28 Holo-, 3 Neo-, 73 Para-, 21 Topotypen) von 31 Arten (siehe Katalog weiter unten). Die meisten Belege bodenlebender Arten sind aus Laubwäldern Süddeutschlands und wurden im Rahmen der bodenzoologischen Untersuchungen des SMNK gesammelt. Aber auch aus Bolivien, Peru, Japan und den USA liegen einzelne Belege vor. Von der Arbeitsgruppe am Max-Planck-Institut für Entwicklungsbiologie in Tübingen wurde Material von tierparasitischen Arten (Pristionchus spp., Strongyloides vituli) mit ausführlichen Angaben zur Präparation und Literatur hinterlegt. Pristionchus pacificus wurde als Satellitenorganismus zu Caenorhabditis elegans, einer von Genetikern als Modellorganismus untersuchten bakterienfressenden Boden-Nematodenart etabliert. Durch den Vergleich dieser beiden Arten kann erforscht werden, wie sich Entwicklungsprozesse – der Übergang vom Ei zum erwachsenen Organismus – im Laufe der Evolution verändern.
Der hier gezeigte digitale Katalog ist ein erstes Beispiel für einen Online-Zugang zu Sammlungsdaten des SMNK aus dem Landesdatenbanksystem imdas pro.
Digitaler Katalog Nematoda
Zuständiger Kurator

Dr. Hubert Höfer, Dipl.-Biol.
Telefon: +49 721 175 2826
E-Mail: hubert.hoefer[at]smnk.de
Nematoden-Arten in der Sammlung
| Familie | Art | SpeciesAuthor | Trophie | Typstatus | Samml.-Nr. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anguinidae | <i>Ditylenchus elegans</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | SMNK-NEMA-0001 | |
| Anguinidae | <i>Ditylenchus elegans</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | SMNK-NEMA-0002 | |
| Anguinidae | <i>Ditylenchus elegans</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | SMNK-NEMA-0003 | |
| Anguinidae | <i>Ditylenchus elegans</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0045 |
| Anguinidae | <i>Ditylenchus parvus</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0044 |
| Anguinidae | <i>Ditylenchus valkanovi </i> | (Andrassy, 1958) | Bodenbewohner | SMNK-NEMA-0005 | |
| Anguinidae | <i>Ditylenchus valkanovi </i> | (Andrassy, 1958) | Bodenbewohner | SMNK-NEMA-0006 | |
| Anguinidae | <i>Ditylenchus valkanovi </i> | (Andrassy, 1958) | Bodenbewohner | SMNK-NEMA-0007 | |
| Aphelenchidae | <i>Laimaphelenchus montanus</i> | Hirling, 1982 | Pflanzenparasit | SMNK-NEMA-0027 | |
| Aphelenchidae | <i>Laimaphelenchus penardi</i> | (Steiner, 1914) | Pflanzenparasit | SMNK-NEMA-0020 | |
| Aphelenchidae | <i>Laimaphelenchus penardi</i> | (Steiner, 1914) | Pflanzenparasit | SMNK-NEMA-0021 | |
| Aphelenchidae | <i>Laimaphelenchus penardi</i> | (Steiner, 1914) | Pflanzenparasit | SMNK-NEMA-0024 | |
| Aphelenchidae | <i>Laimaphelenchus praepenardi</i> | Hirling, 1986 | Pflanzenparasit | SMNK-NEMA-0022 | |
| Aphelenchidae | <i>Laimaphelenchus praepenardi</i> | Hirling, 1986 | Pflanzenparasit | SMNK-NEMA-0023 | |
| Aphelenchidae | <i>Laimaphelenchus sylvaticus</i> | Hirling, 1982 | Pflanzenparasit | SMNK-NEMA-0026 | |
| Aphelenchoididae | <i>Aphelenchoides pini </i> | (Baujard, 1981) | Pflanzenparasit | SMNK-NEMA-0025 | |
| Bunonematidae | <i>Bunonema ornatum</i> | Zell? | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0048 |
| Criconematidae | <i>Criconemella goffarti</i> | (Volz, 1951) | Bodenbewohner | Topotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0113 |
| Criconematidae | <i>Criconemella goffarti</i> | (Volz, 1951) | Bodenbewohner | Topotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0114 |
| Criconematidae | <i>Criconemella goffarti</i> | (Volz, 1951) | Bodenbewohner | Topotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0115 |
| Criconematidae | <i>Criconemella goffarti</i> | (Volz, 1951) | Bodenbewohner | Topotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0116 |
| Criconematidae | <i>Criconemella goffarti</i> | (Volz, 1951) | Bodenbewohner | Topotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0117 |
| Criconematidae | <i>Criconemella goffarti</i> | (Volz, 1951) | Bodenbewohner | Topotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0118 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus aerivorus</i> | (Cobb, 1916) | Tierparasit | SMNK-NEMA-0101 | |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus aerivorus</i> | (Cobb, 1916) | Tierparasit | SMNK-NEMA-0102 | |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus aerivorus</i> | (Cobb, 1916) | Tierparasit | SMNK-NEMA-0103 | |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus americanus</i> | Herrmann, Mayer & Sommer, 2006 | Tierparasit | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0019 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus americanus</i> | Herrmann, Mayer & Sommer, 2006 | Tierparasit | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0020 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus americanus</i> | Herrmann, Mayer & Sommer, 2006 | Tierparasit | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0021 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus elegans</i> | ? | Tierparasit | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0110 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus elegans</i> | ? | Tierparasit | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0111 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus elegans</i> | ? | Tierparasit | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0112 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus exspectatus</i> | Kanzaki, Ragsdale, Hermann, Mayer, Sommer, 2012 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0104 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus exspectatus</i> | Kanzaki, Ragsdale, Hermann, Mayer, Sommer, 2012 | Bodenbewohner | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0105 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus exspectatus</i> | Kanzaki, Ragsdale, Hermann, Mayer, Sommer, 2012 | Bodenbewohner | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0106 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus japonicus</i> | Kanzaki, Ragsdale, Hermann, Mayer, Sommer, 2012 | Tierparasit | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0107 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus japonicus</i> | Kanzaki, Ragsdale, Hermann, Mayer, Sommer, 2012 | Tierparasit | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0108 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus japonicus</i> | Kanzaki, Ragsdale, Hermann, Mayer, Sommer, 2012 | Tierparasit | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0109 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus marianneae</i> | Herrmann, Mayer & Sommer, 2006 | Tierparasit | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0022 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus marianneae</i> | Herrmann, Mayer & Sommer, 2006 | Tierparasit | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0023 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus marianneae</i> | Herrmann, Mayer & Sommer, 2006 | Tierparasit | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0024 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus pauli</i> | Herrmann, Mayer & Sommer, 2006 | Tierparasit | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0025 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus pauli</i> | Herrmann, Mayer & Sommer, 2006 | Tierparasit | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0026 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus pauli</i> | Herrmann, Mayer & Sommer, 2006 | Tierparasit | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0027 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus pseudaerivorus</i> | Herrmann, Mayer & Sommer, 2006 | Tierparasit | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0028 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus pseudaerivorus</i> | Herrmann, Mayer & Sommer, 2006 | Tierparasit | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0029 |
| Diplogasteridae | <i>Pristionchus pseudaerivorus</i> | Herrmann, Mayer & Sommer, 2006 | Tierparasit | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0030 |
| Dorylaimidae | <i>Eudorylaimus badensis</i> | Zell, 1986 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0037 |
| Dorylaimidae | <i>Eudorylaimus pseudobokori</i> | Zell, 1986 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0036 |
| Dorylaimidae | <i>Mesodorylaimus similibastiani</i> | Zell, 1986 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0038 |
| Dorylaimidae | <i>Pungentus porosus</i> | Zell, 1986 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0039 |
| Drilonematidae | <i>Drilocephalobus humophilus</i> | Zell, 1987 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0041 |
| Mononchidae | <i>Parveyellus vorax </i> | Hirling, 1989 | Räuber | SMNK-NEMA-0008 | |
| Mononchidae | <i>Parveyellus vorax </i> | Hirling, 1989 | Räuber | SMNK-NEMA-0009 | |
| Mononchidae | <i>Parveyellus vorax </i> | Hirling, 1989 | Räuber | SMNK-NEMA-0010 | |
| Mononchidae | <i>Parveyellus vorax </i> | Hirling, 1989 | Räuber | SMNK-NEMA-0011 | |
| Mononchidae | <i>Parveyellus vorax </i> | Hirling, 1989 | Räuber | SMNK-NEMA-0012 | |
| Mononchidae | <i>Parveyellus vorax </i> | Hirling, 1989 | Räuber | SMNK-NEMA-0013 | |
| Mononchidae | <i>Parveyellus vorax </i> | Hirling, 1989 | Räuber | SMNK-NEMA-0014 | |
| Mononchidae | <i>Parveyellus vorax </i> | Hirling, 1989 | Räuber | SMNK-NEMA-0015 | |
| Mononchidae | <i>Parveyellus vorax </i> | Hirling, 1989 | Räuber | SMNK-NEMA-0016 | |
| Mononchidae | <i>Parveyellus vorax </i> | Hirling, 1989 | Räuber | SMNK-NEMA-0017 | |
| Mononchidae | <i>Parveyellus vorax </i> | Hirling, 1989 | Räuber | SMNK-NEMA-0018 | |
| Mononchidae | <i>Parveyellus vorax </i> | Hirling, 1989 | Räuber | SMNK-NEMA-0019 | |
| Mononchidae | <i>Parveyellus vorax </i> | Hirling, 1989 | Räuber | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0031 |
| Neotylenchidae | <i>Deladenus crassus</i> | Zell, 1985 | Bodenbewohner | Neotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0047 |
| Neotylenchidae | <i>Deladenus parvus</i> | Zell, 1985 | Bodenbewohner | SMNK-NEMA-0004 | |
| Neotylenchidae | <i>Deladenus parvus</i> | Zell, 1985 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0046 |
| Panagrolaimidae | <i>Panagrolaimus trilabiatus</i> | Zell, 1987 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0040 |
| Plectidae | <i>Plectus communis</i> | Bütschli, 1873 | Bodenbewohner | Neotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0001 |
| Plectidae | <i>Plectus communis</i> | Bütschli, 1873 | Bodenbewohner | Topotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0002 |
| Plectidae | <i>Plectus longicaudatus</i> | Bütschli, 1873 | Bodenbewohner | Neotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0003 |
| Plectidae | <i>Plectus longicaudatus</i> | Bütschli, 1873 | Bodenbewohner | Topotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0004 |
| Plectidae | <i>Plectus longicaudatus</i> | Bütschli, 1873 | Bodenbewohner | Topotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0005 |
| Plectidae | <i>Plectus longicaudatus</i> | Bütschli, 1873 | Bodenbewohner | Topotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0006 |
| Plectidae | <i>Plectus pusteri</i> | Fuchs, 1930 | Bodenbewohner | Neotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0007 |
| Plectidae | <i>Tylocephalus andinus</i> | Zell, 1985 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0033 |
| Plectidae | <i>Tylocephalus becki</i> | Zell, 1985 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0034 |
| Plectidae | <i>Tylocephalus cornutus</i> | Zell, 1985 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0035 |
| Plectidae | <i>Wilsonema andersoni</i> | Zell, 1985 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0032 |
| Strongyloididae | <i>Strongyloides vituli</i> | Brumt, 1921 | Tierparasit | SMNK-NEMA-0104 | |
| Strongyloididae | <i>Strongyloides vituli</i> | Brumt, 1921 | Tierparasit | SMNK-NEMA-0105 | |
| Strongyloididae | <i>Strongyloides vituli</i> | Brumt, 1921 | Tierparasit | SMNK-NEMA-0106 | |
| Strongyloididae | <i>Strongyloides vituli</i> | Brumt, 1921 | Tierparasit | SMNK-NEMA-0107 | |
| Tylenchidae | <i>Filenchus amaritus</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0042 |
| Tylenchidae | <i>Filenchus longicaudatulus</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0043 |
| Tylenchidae | <i>Filenchus resistens</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0012 |
| Tylenchidae | <i>Filenchus resistens</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0013 |
| Tylenchidae | <i>Filenchus resistens</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0014 |
| Tylenchidae | <i>Filenchus resistens</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0015 |
| Tylenchidae | <i>Filenchus resistens</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0016 |
| Tylenchidae | <i>Filenchus resistens</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0017 |
| Tylenchidae | <i>Filenchus resistens</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0018 |
| Tylenchidae | <i>Tylenchus martini</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | Holotypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0008 |
| Tylenchidae | <i>Tylenchus martini</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0009 |
| Tylenchidae | <i>Tylenchus martini</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0010 |
| Tylenchidae | <i>Tylenchus martini</i> | Zell, 1988 | Bodenbewohner | Paratypus | SMNK-NEMA-T 0011 |